How to Wire a Mini-Split System: The Mini-Split & Heat Pump Wiring Guide for HVAC Contractors
Mini-split heat pump systems offer energy efficiency and flexible installation options, but wiring mini-split systems requires precision and adherence to the latest codes. This guide is designed for HVAC contractors as a mini-split wiring reference guide, delivering technical insights and best practices—from determining power requirements to selecting the correct wire gauge and ensuring robust surge protection, to enable you to effectively execute this critical component of mini-split installations. Equip yourself with the expertise to execute safe, reliable, and code-compliant installations.
Understanding Mini-Split Power Requirements & Dedicated Circuits
Mini-split systems often demand a dedicated electrical line integrated directly into the building's electrical panel. It is critical to verify the mini-split power requirements for the system you're installing - Depending on the system capacity, smaller systems (9k–12k BTU) may operate on 115V, while larger mini-splits require a dedicated 208/230V single-phase circuit. Always confirm voltage requirements from the GREE submittal for the specific model. Ensuring that the electrical service panel is correctly sized to handle the additional load is essential for both system performance and compliance with local codes.
Mini-Split Breaker Sizing & Circuit Considerations
Determining the proper mini-split breaker size is key to preventing overloads and ensuring safe operation. Breaker sizing must follow the unit's MOCP as listed on the nameplate and system documentation, in accordance with NEC 440.22.
Selecting the Right Mini-Split Wire & Gauge (What Size Wire for the Mini-Split)
Choosing the correct wire gauge is critical component of mini-split wiring. When evaluating what size wire to use for a mini-split, remember that lower gauge numbers (thicker wires) are required to safely carry higher currents, while higher gauge numbers (thinner wires) suit lower loads. While general ampacity guidelines may reference gauges from 16 to 2 AWG, interconnecting wire must match the conductor size specified on the unit's nameplate and submittal. For many GREE systems, this is 14 AWG copper, 4-conductor, but always verify MCA and follow NEC 310.16 ampacity tables. Do not undersize below system minimums.
Always select UL-listed wiring products that are rated for outdoor exposure. Incorporating mini-split communication wire—designed for transmitting control signals between indoor and outdoor units—further ensures system reliability and operational precision.
Mini-Split Ampacity Guidelines: Determining Mini-Split Wire Size & Power Capacity
Understanding Ampacity
Ampacity refers to the maximum current a specific gauge of wire can safely conduct. Matching the wire gauge to the load is crucial to avoid overheating and potential safety hazards. Installation conditions such as run length and ambient temperature must also be taken into account.
Ampacity Table
| Wire Use | Rated Ampacity | Wire Gauge |
|---|---|---|
| Extension Cords | 13 Amps | 16 Gauge |
| Light Fixtures, Lamps, Lighting Runs | 15 Amps | 14 Gauge |
| Receptacles, 110-volt AC, Sump Pumps, Kitchen Appliances | 20 Amps | 12 Gauge |
| Electric Clothes Dryers, 220-volt Window AC, Built-in Ovens, etc. | 30 Amps | 10 Gauge |
| Electric Stoves | 45 Amps | 8 Gauge |
| Electric Furnaces, Large Electric Heaters | 60 Amps | 6 Gauge |
| Electric Furnaces, Large Electric Water Heaters, Sub Panels | 80 Amps | 4 Gauge |
| Service Panels, Sub Panels | 100 Amps | 2 Gauge |
Practical Tip:
Keep your installation conditions in mind when selecting the proper wiring, as variables like cable run length and ambient temperature can affect effective ampacity.
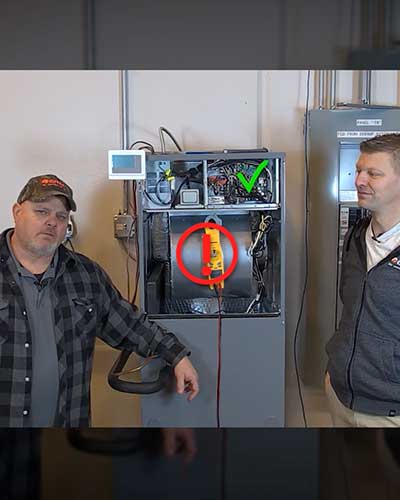
Wiring Mini-Split Disconnects & Key Electrical Components
Mini-Split Core Electrical Components
The reliability of a mini-split installation relies on proper wiring of critical components. The electrical whip, a weatherproof cable assembly, connects power from the disconnect box to the outdoor unit. Additionally, the connecting cable must be 14/4 AWG stranded bare copper conductors (THHN 600V unshielded wire) as recommended by GREE's system documentation. Use shielded cable near RF or EMI transmitting devices to prevent interference.
Ensure there are no breaks or splices in the wiring between the indoor and outdoor units; interconnect conductors must be continuous and connected terminal-to-terminal (1–1, 2–2, 3–3, 4–4). Incorrect or crossed wiring can trigger an E6 error code, causing system malfunction and possible damage.
Mini-Split Disconnect Switch: Fused vs. Non-Fused
A dedicated disconnect switch may be required near the outdoor unit, depending on local codes and regulations. NEC 440.14 requires a disconnect within sight of the outdoor unit. For most mini-splits, a non-fused disconnect is acceptable when the breaker in the panel is sized per MOCP. Verify local code amendments before final selection. This approach minimizes maintenance needs and enhances safety by avoiding issues such as fuse replacement and corrosion.
Protecting Mini-Split Electrical Systems: Surge Protection & Long-Term Safety
Mini-Split Surge Protection Essentials
Electrical surges from lightning or power fluctuations can significantly impact mini-split system performance. Integrating surge protection into your installations is critical to prevent damage and maintain system integrity over time. Surge protection devices should be UL 1449 listed and installed per NEC 242.
Enhancing Mini-Split Reliability Long-Term
Implementing proper wiring practices, using high-quality components, and installing reliable disconnect switches all contribute to a robust mini-split heat pump system that meets both safety standards and performance expectations. These measures not only minimize on-site service calls but also help uphold your reputation as a skilled HVAC professional.
Conclusion & Next Steps for Wiring a Mini-Split System
Successful wiring of mini-split and heat pump systems demands precision, technical expertise, and strict adherence to code requirements. By understanding the specific power needs, selecting the appropriate wire gauge, consulting ampacity guidelines, and implementing effective surge protection, HVAC contractors can ensure every installation is safe, efficient, and built to last.
If you need more in-depth guidance on wiring, or you'd like to explore additional GREE HVAC solutions, be sure to check out our instructional videos and FAQ page for detailed information. If you're a homeowner and want to ensure your mini-split system is installed with proper wiring use our Contractor Locator tool to connect with a GREEComfort-certified specialist in your area for installation, support, troubleshooting, and ongoing mini-split best practices.